from AMW English

Prisoners Lives Matter
by Dwayne “Bim” Staats
-On Wednesday July 8th, Michael Discenko #ME3162 (inmate at S.C.I. Albion, residing in the restrictive housing unit) was tested for COVID-19 because he was due to be released soon (July 15th).
-Sunday July 12th, medical staff (dressed in hazardous suits) went to Michael’s cell to inform him that he’d tested positive for COVID-19, and that another test would be arranged soon.
-Sunday night, a group of us held a meeting to discuss the circumstances. Our conclusion was that the administration was going to quarantine the whole tier without giving the rest of us testing or removing Michael. To counter the inevitable, ten of us decided to go on hunger strike in protest of them leaving Michael on the tier and not giving us testing.
-Monday morning, July 13th, 6:15 am, corrections officer does count and announces that the tier will be quarantined for 14 days… 7:30 am, the ten of us refused our breakfast… 8:00 am, captain and lieutenant come on the tier to investigate why we didn’t eat. They stated that exceptions would be made for us to take showers (which I consider a death trap)… 12:30 pm, inmates from an adjacent tier were brought over to use our showers while we’re “quarantined.”
-Tuesday July 14th, the tier was notified that outside recreation will be available (pretty sure this concession was only offered with hopes that we would start taking trays).
-Wednesday July 15th, 4:30 am, Michael is notified that he won’t be getting tested, and to pack up because they’re releasing him at 6:30 am… 8:00 am, Michael is made aware that they’re (D.O.C.) not putting him on a van. Instead, they’re driving him directly to his house (they never let him warn his family). Michael’s cell was beneath mine, which enabled us to communicate through the vent in our rooms. He expressed that he was a-symptomatic, and like the rest of us in solitary confinement, hasn’t come in close proximity with no one but prison staff. I told him don’t put his family at risk, and when he pulls up to the house, immediately tell his loved ones, “don’t come near me- call the ambulance- I’ve tested positive for COVID-19!”… 1:00 pm, two deputy superintendents and a psychologist came on the tier for a brief moment, then left.
-Thursday morning, July 16th, being that we’ve surpassed 9 consecutive meals, a nurse came on the tier to announce that “those on hunger strike will be charged $5 a day for medical service.” What she failed to mention was, under policy and protocol, the ninth meal signifies that we will be placed in P.O.C. (prisoner observation cells) and monitored by medical and psychologists multiple times throughout the day. True to their nature, policy or protocol wasn’t adhered to. This negligence discouraged a lot of guys from continuing their hunger strike. We were kept in our cells instead of being taken to P.O.C… 11:00 am, medical staff came around to talk to those who remained on hunger strike (Dwayne Staats #NT000, Reuben Henry #HJ3797, Ramon Sanchez #FH7056 and Deshawn Nelson #MN2187). He stated, “Pennsylvania’s governor Tom Wolfe is the only person who can authorize COVID testing for prisoners.” This far, the testing has only been reserved for prisoners who are transferring or getting released. Even those who’ve shown symptoms or have pre-existing conditions are refused testing… 1:00 pm, regional deputies take a tour of the prison. They came to our building, but never step foot on our tier.
-Friday, July 17th, still not put under medical/psychological observation… Guys in hazardous suit spray something in Michael’s old cell. Later on, another inmate is placed inside (yes, we’re still “quarantined”).
-Saturday, July 18th, 11:00 am, medical staff came on the tier, asking to take our vitals (which we all refused) and brag about charging us $5 like it was going into her pocket.
-Sunday, July 19th, 12:30 am, we’re at 18 consecutively missed meals. The guard came around for count and stopped at Reuben’s cell. He kept yelling his name and tapping on the window. This made me get up to see what was going on. Reuben was unresponsive, which caused the guard to alert medical and other officers. A few nurses and guards rushed on the tier. They opened Reuben’s cell and I seen him sprawled out on the floor. Once medical verified “signs of life,” they took him off the tier on a stretcher. About 20 minutes later, he walks back on the tier and the guards secure him back in the cell. Medical said he passed out because of dehydration and low sugar levels… 1:00 am, Reuben is brought peanut butter and jelly sandwiches (but still not put under observation). 6:00 pm, medical personnel finally follows up on Reuben (who still refused trays) and the rest of us who was on hunger strike… To be continued.
In closing, there is a total disregard for prisoners lives that needs immediate attention. Furthermore, all the guys who ended their hunger strikes are now being retaliated against by the prison staff or administration for having the audacity to protest. Until next time, be easy and take care!
Power is the people!
-Bim
Dwayne Staats #NT0000
S.C.I. Albion
P.O. Box 33028
St. Petersburg, FL 33733
P.S. I ain’t on no suicide mission and I ain’t gone let these people get the satisfaction of killing me!




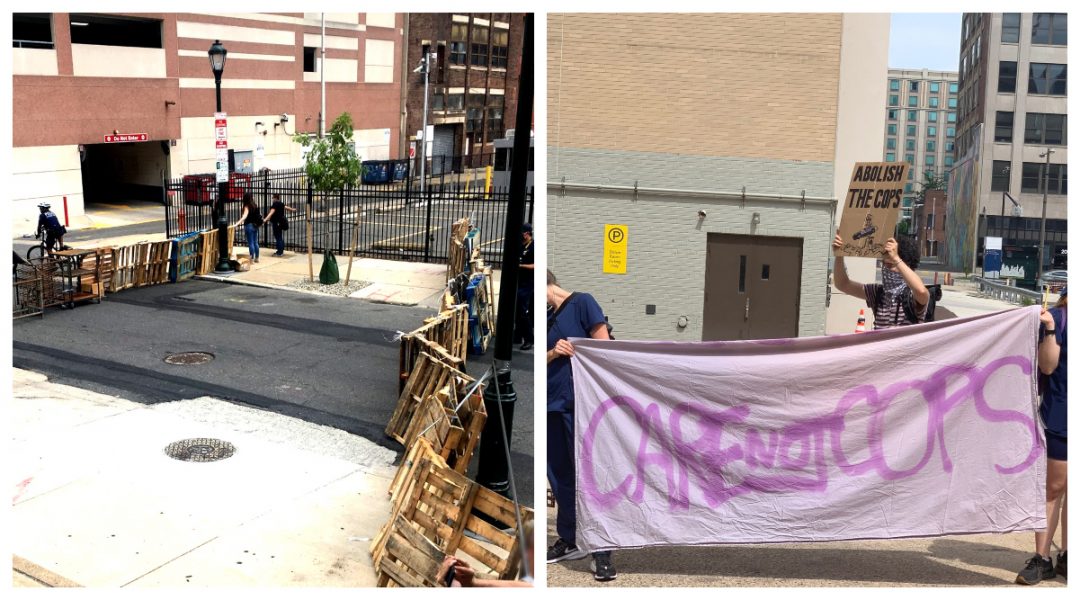
 On Saturday, June 27th, healthcare workers and community members in Philadelphia held a temproary occupation of the shuttered Hahnemann Hospital. Following a rally at the City Hall, a crowd of around 100 people marched north to the empty hospital tower, erected canopies, tables, and chairs, and began to attend to patients who had joined the march and were eager to receive care. Before it was closed in the summer of 2019 it predominantly treated Black poor and working class people of Philadelphia, with social service providers housed in the same tower as doctors and specialists. Its most recent owner, the banker turned heathcare investor Joel Freedman, had bought it only a year before, and when he determined it wasn’t profitable enough he filed for bankruptcy, laid off around 800 unionized nurses, and deprived the underserved population of Philadelphia of their primary source of care.
On Saturday, June 27th, healthcare workers and community members in Philadelphia held a temproary occupation of the shuttered Hahnemann Hospital. Following a rally at the City Hall, a crowd of around 100 people marched north to the empty hospital tower, erected canopies, tables, and chairs, and began to attend to patients who had joined the march and were eager to receive care. Before it was closed in the summer of 2019 it predominantly treated Black poor and working class people of Philadelphia, with social service providers housed in the same tower as doctors and specialists. Its most recent owner, the banker turned heathcare investor Joel Freedman, had bought it only a year before, and when he determined it wasn’t profitable enough he filed for bankruptcy, laid off around 800 unionized nurses, and deprived the underserved population of Philadelphia of their primary source of care.