Submission
At the beginning of the summer some Philly anarchists were interviewed by some German comrades regarding recent events in the States. This is the transcript of that interview.
How do you explain that the riots and social unrest spread and
intensified so fast in the last month? Do you think the lockdown had an influence on it?
0: I think that coronavirus had a lot to do with it. Before corona people around the world were in revolt and the US was just watching. Hong Kong and Chile and Canada seemed to be going off and people were paying attention to that and learning and talking about it. When the pandemic hit people here lost a lot of work and there was not as much for anyone to do. The protests and riots were a much appreciated break from the quarantine, people got to finally go outside and be together after months, and it was more accessible than if everyone had to be at work.
In other circumstances people would be tied up in work, school, and a larger social life. When the uprising started there weren’t too many places you could be, you could stay home, go for a walk, or go to a riot or protest.
X: I agree, and also think the tension has been building up for some time; and I mean that in a bigger sense than the usual upheaval as pressure release. Many have said that these have been the biggest riots in the States since Martin Luther King Jr was assassinated in the 60’s – so I think in addition to the obvious white supremacy, and the stagnation and poverty under quarantine, there is a growing existential dread from the very real threats of global pandemics, climate catastrophe, fascist terror, rape culture, and many other such things that similarly propelled those global revolts several months ago.
&: Yes, I agree coronavirus was part of the building up. It was a strange, nonlinear build up where many people spent the weeks before trying to figure out how to adapt to isolation and social distancing. Under normal circumstances, you can fantasize about what you would do when the time came to rebel and even speculate about likely time to act. For me, anyway, the virus creates circumstances where it was almost impossible to imagine regularly leaving the house, let alone taking the streets. The virus laid the groundwork for some of the conditions of the riots, creating almost strike-like conditions. But at the same time, there was no clear path to take advantage of them. On the one hand, I think this meant that the activist organizers were not immediately positioned to channel the events in Minneapolis into an ongoing campaign or strategy – allowing for better conditions for a riot. On the other hand, when people watched the news coming out of Minneapolis from their “pods,” they saw these massive self-organized crowds as if they were seeing them for the first time. The sudden, renewed ability to imagine being in the streets together was like realizing how thirsty you are when someone offers you a drink.
It didn’t hurt that, once everyone met up in the streets, many of them were wearing masks. The riot happened right around the time that masks became a normal precaution. Wearing masks took a while to catch on and then kind of went out of style once it got really hot. I hope it gets normalized again.
How was the experience in your local context?
0: In Philly things went wild the last Saturday of May. Center City had intense rioting and looting. People set fire to police cars and stores, fought with the police, and broke into and took merchandise from so many stores. Graffiti against the police was everywhere and many banks were smashed. That night and the next day the rioting spread to other neighborhoods. Stores and malls around the city were looted for the next few days and nights. 52nd St – a main commercial street in West Philadelphia – was the site of clashes with the cops and looting. After that the National Guard came to the city and things slowed down some. There are still protests everyday all over the city but they are calmer and less combative than the first weekend.
Other struggles also escalated briefly while the rioting happened. A labor struggle at a cafe in West Philadelphia was intensified when the cafe was vandalized multiple times and had to end up closing. Gentrifiers in West and South Philly were attacked during the nights immediately following the riots. Mutual aid projects related to homelessness and coronavirus continued while shifting their attention to the uprising.
Housing and homelessness related organizing has seen a big escalation. On one hand a tent camp has been set up right outside of Center City and is growing everyday. On the other hand individuals and families are squatting in city owned properties as a reaction to corruption in the Philadelphia Housing Authority. Both the camp and the squatters are asking for permanent low income housing. This kind of thing would have seemed much more difficult without the context of the uprising.
X: Yeah, there were a few wildcat strikes happening at different businesses that seemed to fit into the slow reduction of combativeness, with at least one still happening. The farther we get from the initial rupture, for that matter, the smaller and more trivial noted actions become.
&: In a similar vein, healthcare workers, anarchists and others tried to occupy an abandoned hospital the other day. It was to be an occupation of the exterior of the building and provide a free clinic. The Hahnemann hospital notoriously remained closed during the pandemic because the investment banker who owns it refused to rent it for an affordable price. The demonstration was more aggressive than most pre-riot demonstrations: the crowd shouted anti-police chants and barricades were rapidly set up to block police in the street leading to the hospital. However, the turn out was much smaller than expected and the police response came swiftly. The occupation was abandoned before the riot police got into formation. So, there are continued attempts at escalation even while crowds are dwindling.
You think anarchists were ready (analytically and materially) and could seize occasions to escalate the revolt?
0: I think many anarchists were surprised at the speed and intensity of the revolt. Many anarchists participated and brought their special knowledge and skills to the table, but I do not think that anarchists were the ones escalating the revolt for the most part. Anarchists out during the revolt were fighting and rioting shoulder to shoulder with other people, many of whom were much more prepared to escalate the situation than anarchists were.
X: We were in the mix, sharing some practical on-the-ground skills, but to some degree I think we were just chasing the intensity. I agree we largely weren’t the ones escalating the revolt, and in fact some participants seemed distrustful of us. There’s also not much of a culture of rioting here, in part because of the whitewashing of history that we’ve long contested, but we don’t have enough of a reach for that to make a significant impact. I think those combination of things, too, meant we weren’t always thinking strategically about our strengths or the state’s weaknesses – though again, in the grand scheme of things, this wouldn’t necessarily prolong the revolt nor significantly weaken our opponents.
&: Yes, I agree. The riot unfolded in a way that exceeded many anarchists’ skills and experience, including my own. At first, the major demonstration followed a familiar – if unforeseen – pattern: a large march made it possible for small groups to fight police and destroy cop cars. I was actually surprised by the amount of cop cars burned and the number of people taking part. At the same time, it was the kind of action – a combination of march and riot – that anarchists are known for in America. It is impossible to say if anarchists were responsible for some of the initial escalations during the demonstrations. What’s clear is that the riots quickly became too decentralized for any one group to be at the center. The looting began, to my knowledge, in the streets near the initial demonstration. But once it began there was a proliferation of flashpoints. It was sometimes difficult to find out where things were happening and, for some time, things were happening at multiple sites at once. The riots took on a shape unlike anything I had been in before.
What forms of recuperation are used and by which actors? And are they successful to channel the uprising back into reformist/democratic discourses?
0: The police and activists sympathetic to them were seen kneeling during demonstrations, a symbolic gesture against police brutality. Many liberals and people on the left are using the popular dissatisfaction to advocate for voting, as though a new politician will change the police. Less often but still present are families of some of the victims of those killed by this racist society who ask that the police investigate and bring to justice the killers.
More insidiously there is a recuperation that masks itself as anti-racism. There are people (black and not) who urge white and non-black people to follow black leadership. The black leadership these people are talking about is always more conservative than the uprising itself. The leadership is always moderate, riotous youth or black revolutionaries are of course never referred to as leadership by these people. This kind of narrative is effective at stopping people who would otherwise take radical or combative action (alongside black people who are already doing the same) by pushing them to feel guilty for not obeying the wishes of black moderates.
&: Not only are riotous youth and black revolutionaries not considered “leadership,” they have been intentionally excluded from the narrative. One way this happens is by replacing them in the narrative with agent provocateurs. Every time something gets broken, burned, or out of control, there’s a corresponding movement to blame it all on agents, provocateurs, outside forces etc. This is in some ways a strategy of recuperation since it seems to be motivated by the desire to separate these bad actors from the respectable protests and their demands. Yet, it’s not exactly a strategy since the there really isn’t a fully-formed activist strategy to recuperate the riots yet. Instead, this attempt to recuperate recent events treats the rioters as a confusing mish-mash of conspiracies. These conspiracy theories stand in for the absent recuperation strategy. Conspiracy theories are spread by a variety of actors–they are not a cohesive group. They are a reserve army of a yet-to-be-initiated activist campaign.
What role play abolitionist ideas (to abolish the police, prisons, etc.) ideas that may be in favor of riots since they bring a topic into focus but at the end of the day pursue a /political/ goal? Is there also a discourse (on the street) around destruction of all power structures?
0: Abolitionist ideas have played a strong role in the uprising. Although the initial cry rang out as “fuck 12” it was quickly turned to “defund/disempower/disband/abolish the police”. Many of the abolitionists imagine on one hand asking people around them to pick up strategies for dealing with life without the police (transformative justice, not snitching, bringing in social workers, etc) and on the other hand asking the government and institutions to disempower police (less money for police, no police in schools, less equipment for police, etc). Many abolitionists understand the rage of people attacking the police but do not imagine that people will remove police themselves and rely on making demands.
Much of the graffiti that came out of the revolt was more pointedly for the destruction of the police. Slogans like “fuck 12,” “acab,” “kill cops,” and “fuck the police,” were all over the walls. The people who push to destroy as opposed to abolish the cops are less present in the discourse but were very present in the street during the rioting. The anarchists continue to push an anti-police anti-prison narrative via a recent noise demonstration outside a prison and via posters and graffiti.
What does it mean that individuals or groups be they militias, gangs or maybe even revolutionaries are armed that heavily in such a situation?
X: We don’t see a lot of it, by our standards, and a lot of it is posturing for the sake of an image. Gun culture is also far less of a thing on the left, or even in anarchist circles.
Much of the “gun control” legislation that has been passed historically serves to disarm the most marginalized people, not least of all Black militants. In the state of North Carolina, for that matter, where it is legal to walk around carrying a gun, a group of black men were recently arrested for doing so at a protest, while there were many instances of white conservatives showing up armed and shaking hands with police.
When it is more than a symbolic gesture toward militancy, though, it often shows how much of a disadvantage those against the establishment are at, since even civilian establishment supporters are much better armed than us and often more willing to use violence. In a larger sense, we see a far-right tendency among mass shooters who obviously cannot be reasoned with. As such, it should mean that anarchists should be better armed and trained, but there are also a lot of hurdles to legally being allowed to carry a weapon most places – including police approval in our city (for which you can be denied based on “character” alone).
What comes next: generalized insurrection, civil war or smart dictatorship?
X: The United States has been extremely successful in pacifying its citizens over the last century; even those moments of rupture that do occur usually serve as more of a pressure release valve followed by reforms that sneak in additional criminalization of protest tactics (i.e. The Anti-Riot clause of the Civil Rights Act of 1968). The surveillance state continues to expand, furthering a smart dictatorship as democracy, but tensions continue to build.
The proliferation of radical ideas (i.e. abolition) in the mainstream is a useful basis of discussion, but as always it’s coupled with a demonization of anarchists, limiting our impact.
Unfortunately, even though I never want to defer to politicians or their lackeys (voters), I think the presidential election in November will be a deciding factor. If the incumbent is reelected we might see attempts at insurrection, whereas if he loses we might see armed white supremacists take the streets trying to kick off a civil war – barring other significant crises derailing everything before then.
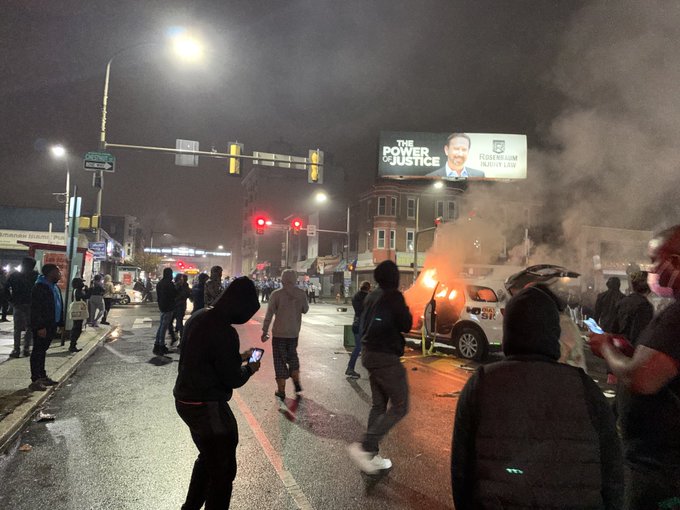
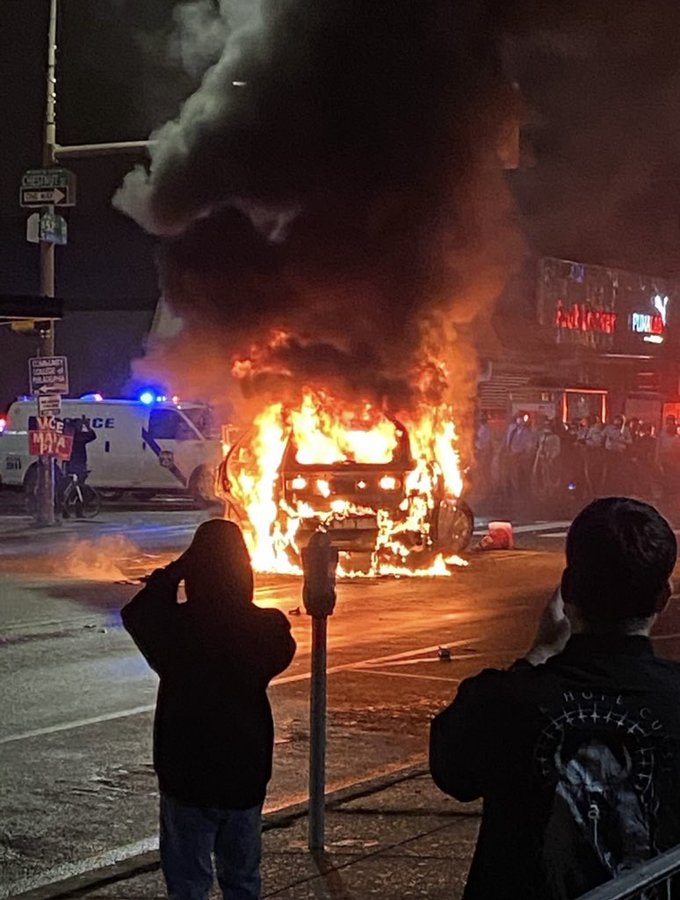
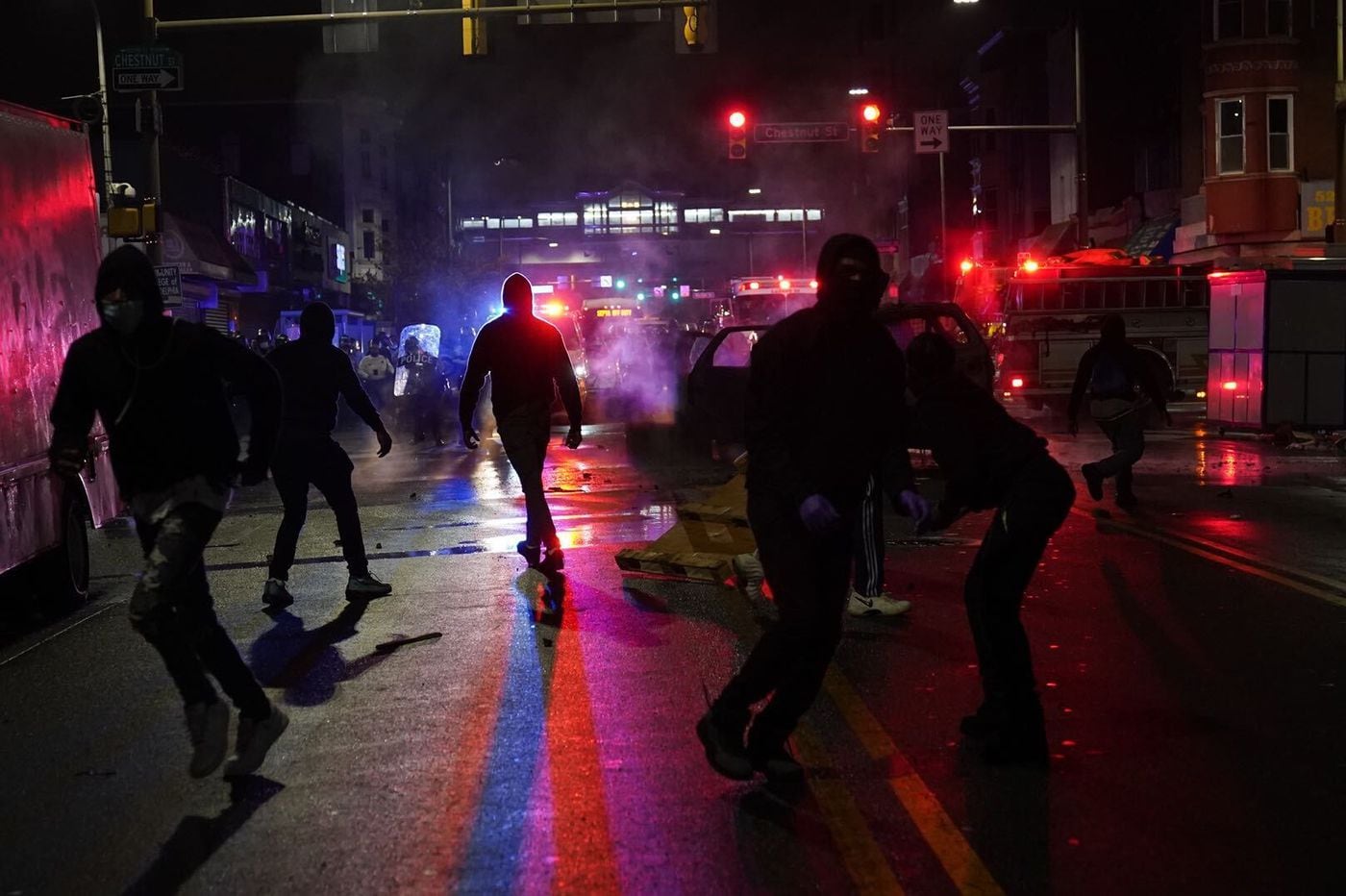













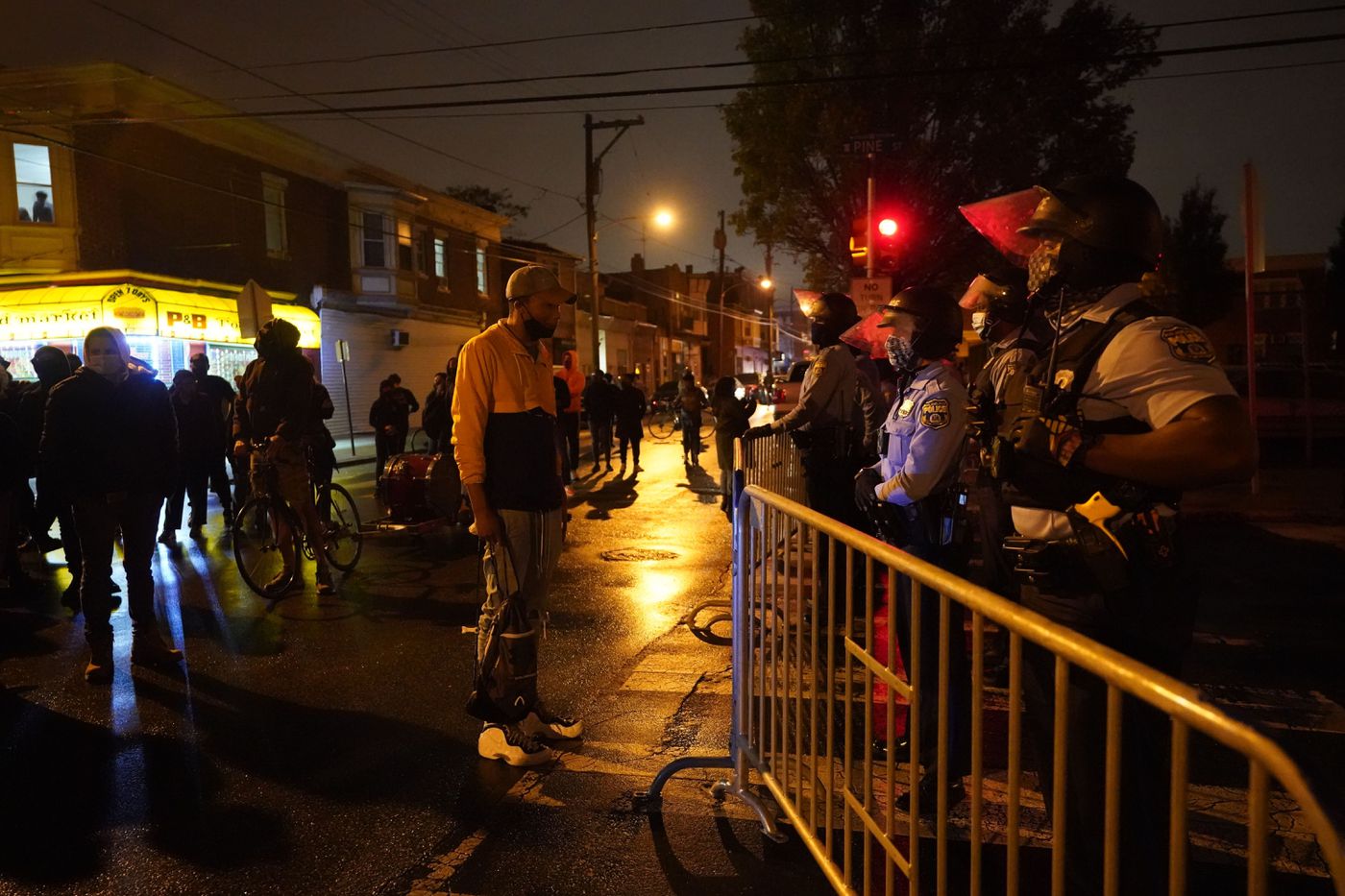












 A police vehicle on fire near the on-ramp of the Vine Street Expressway. (Saturday, May 30).
A police vehicle on fire near the on-ramp of the Vine Street Expressway. (Saturday, May 30). The same area one week later (Municipal Services Building where Rizzo had stood is to the right of photo.)
The same area one week later (Municipal Services Building where Rizzo had stood is to the right of photo.) After a crew painted over the mural of former top cop and mayor Frank Rizzo early Sunday morning, all that remained was the street sign on the upper right hand side.
After a crew painted over the mural of former top cop and mayor Frank Rizzo early Sunday morning, all that remained was the street sign on the upper right hand side.